Smart Cities and Infrastructure Monitoring
Safer, cleaner and greener with IoT
CHALLENGES
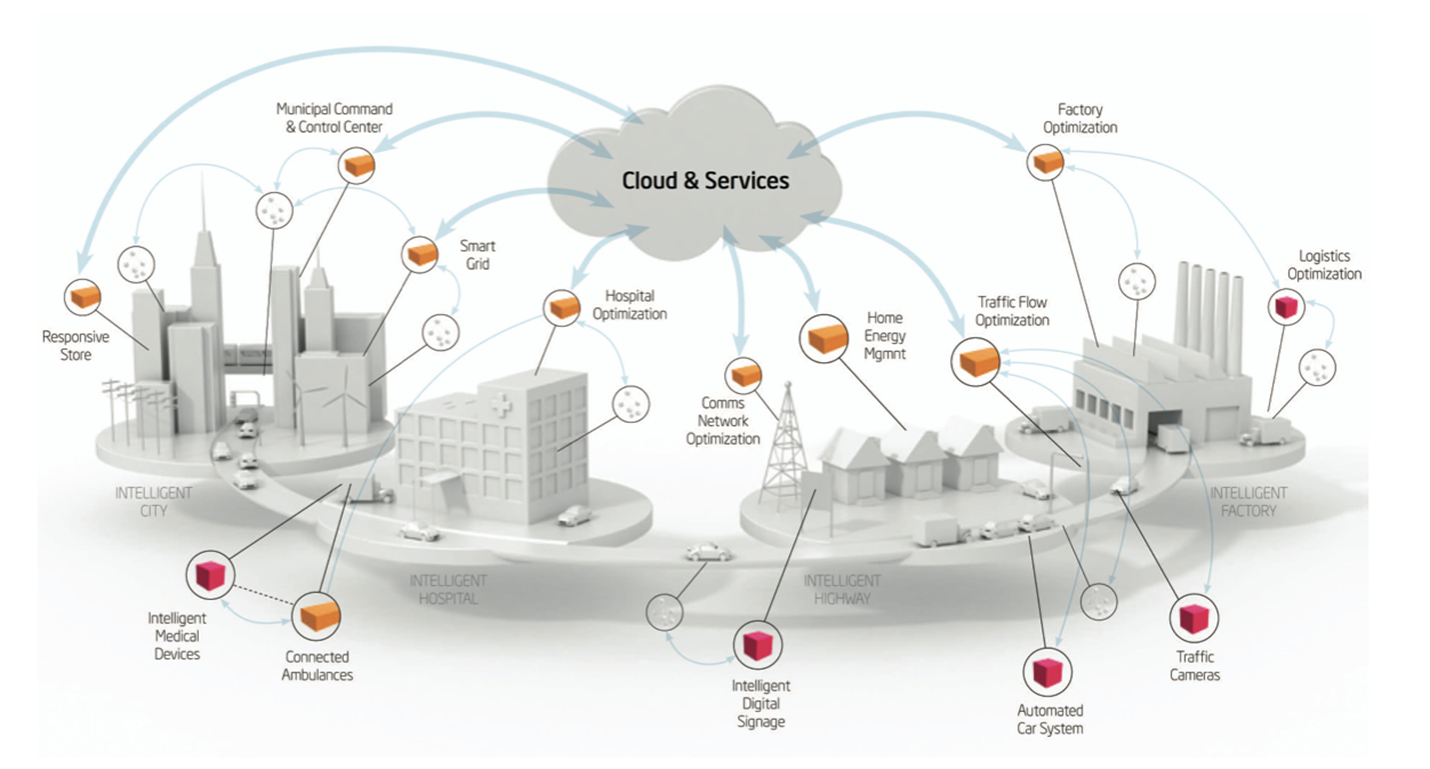
In the city of Turin we are developing a service delivery platform that integrates City Information System with Internet of Things technologies for sensing and actuation to support green and sustainable Smart City applications. The collected IoT Data is integrated with the business and organizational data in the city´s operational systems. This enables improved and more efficient business processes that will help the city deliver better services to the citizens. The ALMANAC Smart City Platform collects, aggregates, and analyses real-time data from heterogeneous sensors and actuators to support Smart City processes. CNet is researching and developing a federated storage architecture for big data processing and advanced resource and service catalogue functions to support semantic interoperability of heterogeneous resources, devices, and services.
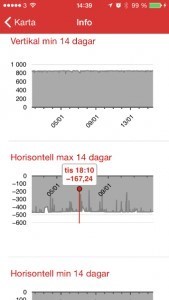
Roads and bridges are critical infrastructures in a city. Repairs and maintenance work immediately effects the traffic situation. Manual inspections of road and bridge conditions are costly. These problems are tackled by the IoTBridge consortium in which CNet is a part. We are combining different types of sensors embedded into wireless sensor networks which exchange information utilising cloud technologies. Data on the use of bridges and status of various parts is analysed to optimise inspection intervals and maintenance to reduce the costs for upkeep and ensure safety. A first installation of the system is done at the new Årsta Bridge, a railway bridge in Stockholm. The vertical and horizontal acceleration as well as temperature are continuously measured, and made available to bridge engineers and inspectors in smart phone apps.
Together with the cities of Turin and Manchester we are investigate how to optimize the energy system in a city and its different districts. This involves using IoT middleware to combine real-time data from sensors and meters with different data sources like Building Information Systems, Geographical Information Systems and Energy Performance data. Energy Benchmarking and Forecasting are under development as well as sophisticated visualization techniques to increase users’ interest and awareness of their energy consumption.

